What Is The Direction Of Velocity For A Satellite

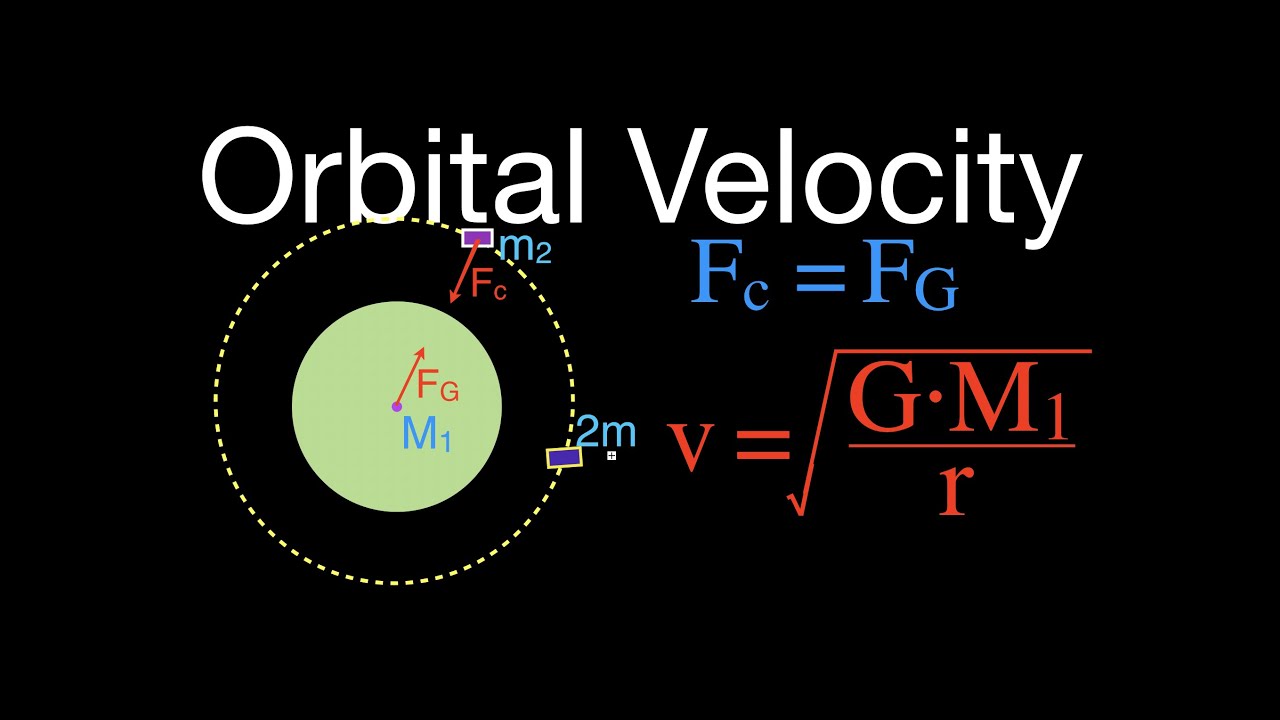
The force and the acceleration are centripetal and they both point from the position of the satellite toward the center of the earth.
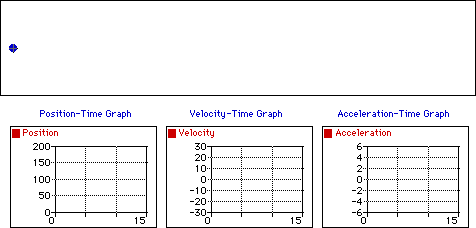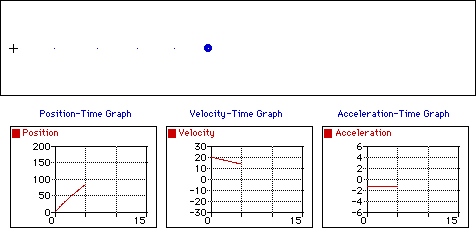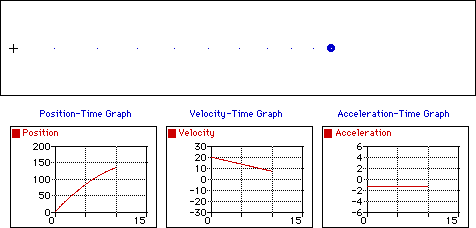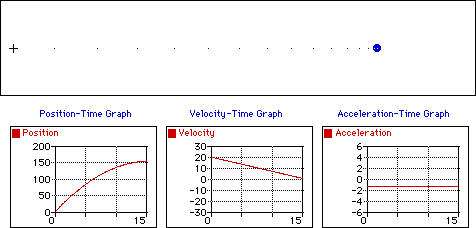
What is the direction of velocity for a satellite. The term can be used to refer to either. Without gravity the satellite s inertia would carry it off into space. The velocity of a satellite is in tangent to the circle of orbit. By steven holzner.
R r h. Now this r is the sum of the radius of the earth r and the height h of the satellite from the surface of the earth. Orbital velocity is the velocity needed to achieve balance between gravity s pull on the satellite and the inertia of the satellite s motion the satellite s tendency to keep going. Since velocity is made up of a speed and a direction you might also say that it changes the satellite s velocity.
This is approximately 17 000 mph 27 359 kph at an altitude of 150 miles 242 kilometers. Now equating equation 1 and 2 we get f g f c g m m r 2 mv 2 r. The acceleration of the satellite is directed towards the focus of the ellipse. Remember the satellite is constantly accelerating towards the center of the circle orbit.
This is because of the constant acceleration due to gravity towards the center of mass center of earth. 6 a satellite in outer space is moving at a constant velocity of 21 1 m s in the y direction when one of its onboard thruster turns on causing an acceleration of 0 290 m s 2 in the x direction. Once more this net. The acceleration lasts for 43 0 s at which point the thruster turns off.
In space gravity supplies the centripetal force that causes satellites like the moon to orbit larger bodies like the earth. Thanks to physics if you know the mass and altitude of a satellite in orbit around the earth you can calculate how quickly it needs to travel to maintain that orbit. The velocity of the satellite is directed tangent to the ellipse. The direction of the satellite s acceleration is not tangential to the circular motion but rather perpendicular to its velocity towards the centre of the earth.
In gravitationally bound systems the orbital speed of an astronomical body or object e g. V is the linear velocity of the satellite at a point on its circular track. The gravitational force of the earth on the satellite is providing the centripetal force.